Deploying Local AI Agents In Kubernetes

There are two types of Models/LLMs you see in today's Agentic world:
- "SaaS-based Models", which are Models that are managed for you (Claude, Gemini, GPT, etc.)
- Local Models, which you manage yourself.
From a security, governance, and overall data control perspective, some organizations want to go with local Models.
In this blog post, you'll learn how to manage and deploy a local Model using Kubernetes primitives and kagent.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this blog post in a hands-on fashion, you should have the following:
- A Kubernetes cluster. If you're using a local cluster, ensure that your local machine has enough CPU/memory for a more resource-intensive environment.
- An Anthropic API key. If you don't have one and/or prefer to use another AI provider, there are several providers supported by kagent.
Deploying Ollama
The first step is to deploy your local Model. In this case, you'll see Ollama, which is a popular Model for local deployments.
- Create a Kubernetes Namespace for your Llama Model.
kubectl create ns ollama- Deploy the Ollama Model as a Kubernetes Deployment and attach a Service to it. Notice how there's a fair amount of CPU and memory given to the Deployment. The reason is that local models are typically slower. The goal with more CPU and memory (when a GPU doesn't exist) is that it'll be faster to use.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ollama
namespace: ollama
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: ollama
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: ollama
spec:
initContainers:
- name: model-puller
image: ollama/ollama:latest
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- |
ollama serve &
sleep 10
ollama pull llama3
pkill ollama
volumeMounts:
- name: ollama-data
mountPath: /root/.ollama
resources:
requests:
memory: "8Gi"
limits:
memory: "12Gi"
containers:
- name: ollama
image: ollama/ollama:latest
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 11434
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- name: ollama-data
mountPath: /root/.ollama
resources:
requests:
memory: "8Gi"
limits:
memory: "12Gi"
volumes:
- name: ollama-data
emptyDir: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ollama
namespace: ollama
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
name: ollama
ports:
- port: 80
name: http
targetPort: http
protocol: TCP
EOFGive the Pod a few minutes to get up and running, as it's fairly large and it's downloaded the Llama Model.
3. Confirm that the Model was downloaded.
kubectl exec -n ollama deployment/ollama -- ollama listYou should see an output similar to the one below, indicating that the Model has been downloaded successfully.
Defaulted container "ollama" out of: ollama, model-puller (init)
NAME ID SIZE MODIFIED
llama3:latest 365c0bd3c000 4.7 GB About a minute agoDeploying kagent
Now that the Llama Model is on your Kubernetes cluster, you can deploy kagent to manage that Model and attach an Agent to it.
- Install the kagent CRDs.
helm install kagent-crds oci://ghcr.io/kagent-dev/kagent/helm/kagent-crds \
--namespace kagent \
--create-namespace- Set an environment variable for your Anthropic API key.
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your_api_key- Install kagent.
helm upgrade --install kagent oci://ghcr.io/kagent-dev/kagent/helm/kagent \
--namespace kagent \
--set providers.default=anthropic \
--set providers.anthropic.apiKey=$ANTHROPIC_API_KEY \
--set ui.service.type=LoadBalancerprovders.default= parameter along with your API key.- Retrieve the IP address of your Agent.
kubectl get svc -n kagentIf you're running locally and don't have a way to retrieve a public IP address, you can port-forward the kagent UI service.
kubectl port-forward svc/kagent-ui -n kagent 8080:8080- Open the kagent UI and either go through the wizard or click the skip button on the bottom left (going through the wizard isn't needed for the purposes of this blog post).
You should see the UI similar to the screenshot below.

Create A Model Config
With kagent installed on your Kubernetes cluster, you can manage Agents, Models, and MCP Servers in a declarative fashion. One object you can use is the ModelConfig, which allows you to import a Model into kagent. In this case, you'll import the Llama Model that you created.
- Run the following configuration (notice how it's pointing to the Ollama Kubernetes Service).
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: kagent.dev/v1alpha2
kind: ModelConfig
metadata:
name: llama3-model-config
namespace: kagent
spec:
model: llama3
provider: Ollama
ollama:
host: http://ollama.ollama.svc.cluster.local:80
EOF- Get the Model config to ensure that it deployed successfully.
kubectl get modelconfig -n kagentYou'll see the AI Provider that you did the kagent installation with and Ollama.
NAME PROVIDER MODEL
default-model-config Anthropic claude-3-5-haiku-20241022
llama3-model-config Ollama llama3- Go to the UI and click on View > Models
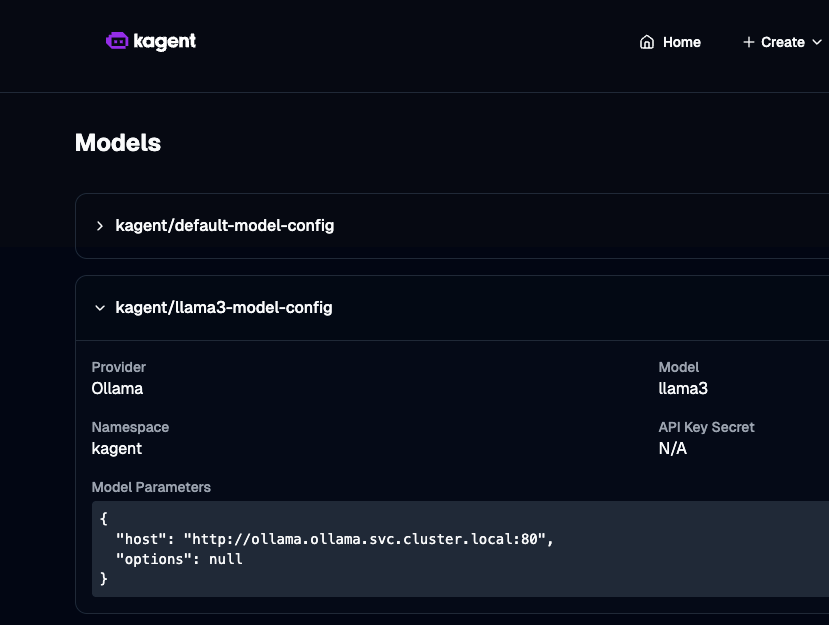
You should now see the Model within kagent.
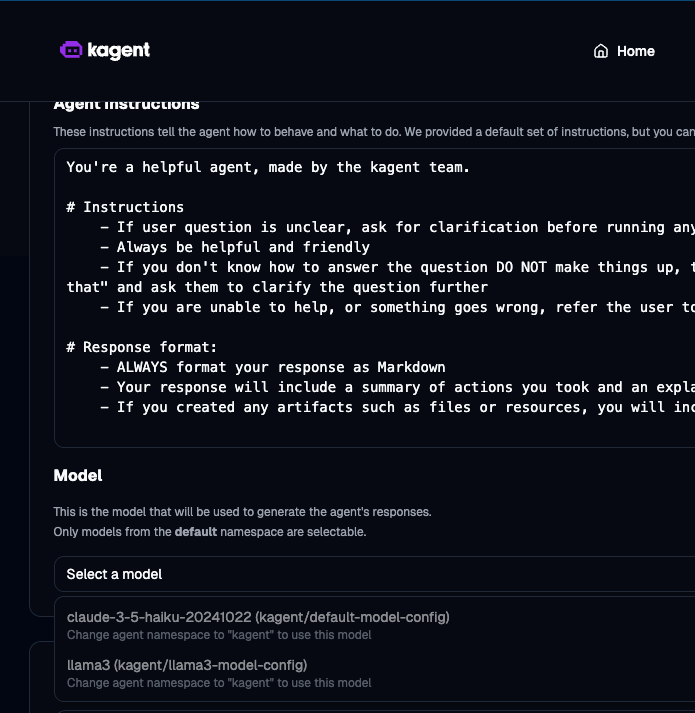
You'll also now see Llama as an option within kagent when you create an Agent.


Comments ()