Building Resilience Into Agents and LLMs
Understanding how any environment will hold up under load is crucial. Whether it's an eCommerce site, a public-facing application, or internal workloads, you want to ensure that "whatever you throw at it" will result in a highly scalable, resilient, self-healing environment.
When Agents and Models/LLMs are running within Kubernetes, it's no different.
In this blog post, you'll learn how to test the resiliency of Agentic Pods running LLMs within Kubernetes.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this blog post from a hands-on perspective, you'll need the following:
- A Kubernetes cluster
- An Anthropic API key or another provider that is supported by kagent. You can find the full list here.
What Is Chaos Engineering
There are two major goals for any system:
- Get it working
- Keep it working
Regardless of whether the system(s) are in the cloud, on-prem, virtualized, or AI-related, the goal is to keep the workloads up and operational. The question is, how do you know if your system or workloads can "take a hit"? If they're under serious load (e.g - an eCommerce site on Cyber Monday) or if a workload goes down (e.g - A Pod goes down), is your system resilient enough to recover?
That's where Chaos Engineering/Testing comes into play.
It's the act of creating controlled tests (usually called Experiments) and running them against your system to ensure that systems and workloads stay up, regardless of the situation that occurs.
There are several tools available, but in this blog post, you'll see Chaos Mesh used. Another popular Chaos Engineering tool is Gremlin if you'd like to try out another solution after reading this article.
Spinning Up Kagent
In this section, you'll learn how to install kagent in your Kubernetes cluster. If you want a more in-depth blog post on this topic, you can find it here.
- Install the kagent CRDs.
helm install kagent-crds oci://ghcr.io/kagent-dev/kagent/helm/kagent-crds \
--namespace kagent \
--create-namespace- Specify your Anthropic API key.
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your_api_key- Install kagent
helm upgrade --install kagent oci://ghcr.io/kagent-dev/kagent/helm/kagent \
--namespace kagent \
--set providers.default=anthropic \
--set providers.anthropic.apiKey=$ANTHROPIC_API_KEY \
--set ui.service.type=LoadBalancerInstalling Chaos Mesh
With kagent installed, it's time to install Chaos Mesh, the tool you'll use for Chaos Engineering in your AI environment.
- Pull down the Chaos Mesh repo.
helm repo add chaos-mesh https://charts.chaos-mesh.org- Depending on the runtime you're using, your installation may differ. You can see all of the Helm installations per runtime here. For the purposes of this blog, an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), cluster was used, so the Containerd runtime is present.
helm install chaos-mesh chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh \
-n=chaos-mesh \
--set chaosDaemon.runtime=containerd \
--set chaosDaemon.socketPath=/run/containerd/containerd.sock \
--create-namespace- Ensure Chaos Mesh is installed.
kubectl get pods -n chaos-mesh- Port forward the UI so you can see the Chaos Mesh dashboard.
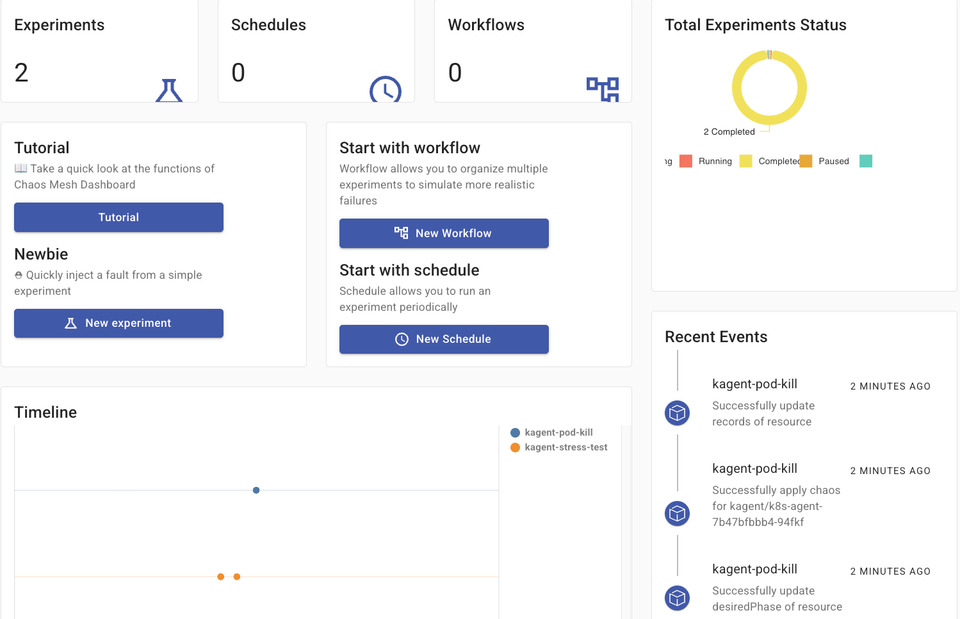
kubectl port-forward -n chaos-mesh svc/chaos-dashboard 2333:2333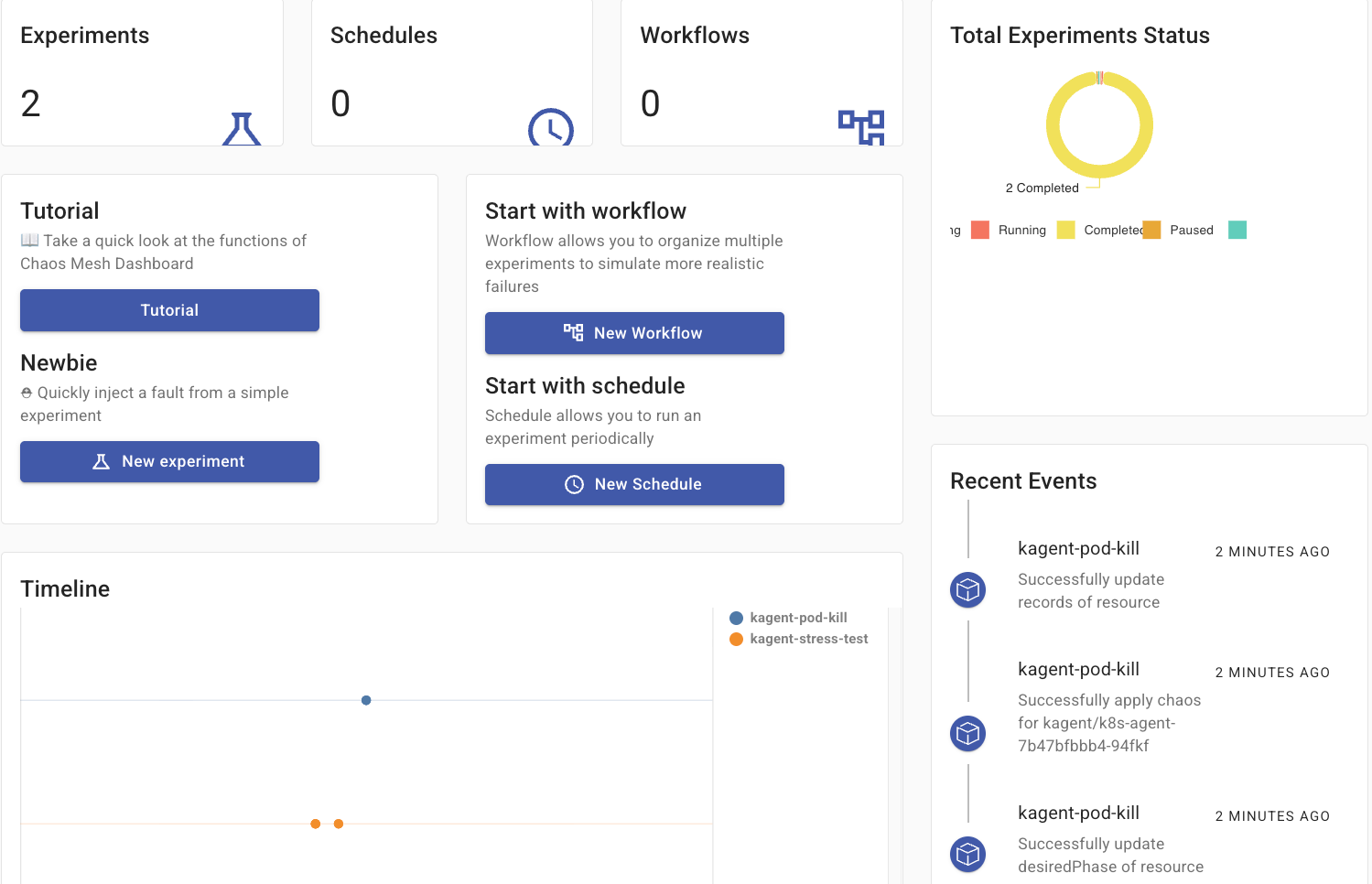
Configuring The Dashboard
For Chaos Mesh to be able to interact with Pods running in a particular Namespace to do chaos testing, it needs access to said Pods.
- When you open the dashboard, the first thing you'll see is the Token Generator. Run through those configs. You can see an example below:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
kind: ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
namespace: kagent
name: account-kagent-manager-htket
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: kagent
name: role-kagent-manager-htket
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "namespaces"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
- apiGroups: ["chaos-mesh.org"]
resources: [ "*" ]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete", "patch", "update"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: bind-kagent-manager-htket
namespace: kagent
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: account-kagent-manager-htket
namespace: kagent
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: role-kagent-manager-htket
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
EOFkubectl create token account-kagent-manager-htket -n kagentWhen you run the create token command on your terminal, you'll see a Token output. Copy/paste that into Chaos Mesh.
Once you do that, you'll be authenticated.
Creating Experiments
With Chaos Mesh installed, you can start to create Experiments, which are the scenarios/tests you want to run. For example, if you want to test what happens if an Agent Pod goes down, will it recover?
In this section, you'll do some tests against the k8s-agent Agent Pod.
- Get the Pod name of your
kagent-agentPod.
kubectl get pods -n kagent- Create an Experiment for stress testing the Pod. Ensure you replace the name of the k8s-agent Agent Pod in the following Manifest.
The experiment below is a stress test.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: chaos-mesh.org/v1alpha1
kind: StressChaos
metadata:
name: kagent-stress-test
namespace: chaos-mesh
spec:
mode: one
duration: '120s'
selector:
namespaces:
- kagent
pods:
kagent:
- k8s-agent-xxxx-xxxx # Replace with your specific pod name
stressors:
cpu:
workers: 2
load: 80
memory:
workers: 2
size: '512MB'
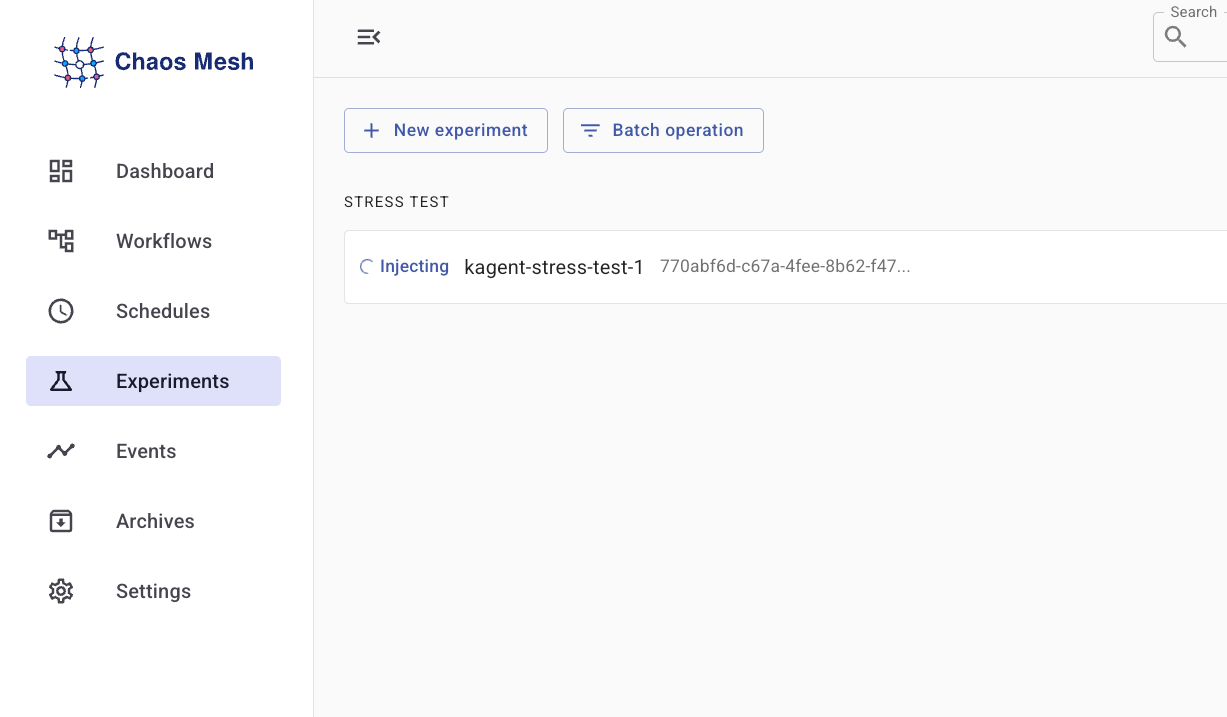
EOF- When you open the dashboard, you'll see that the Experiment is running.
- Opening up the Experiment, you can see what is running, what tasks it's going through, and the results.
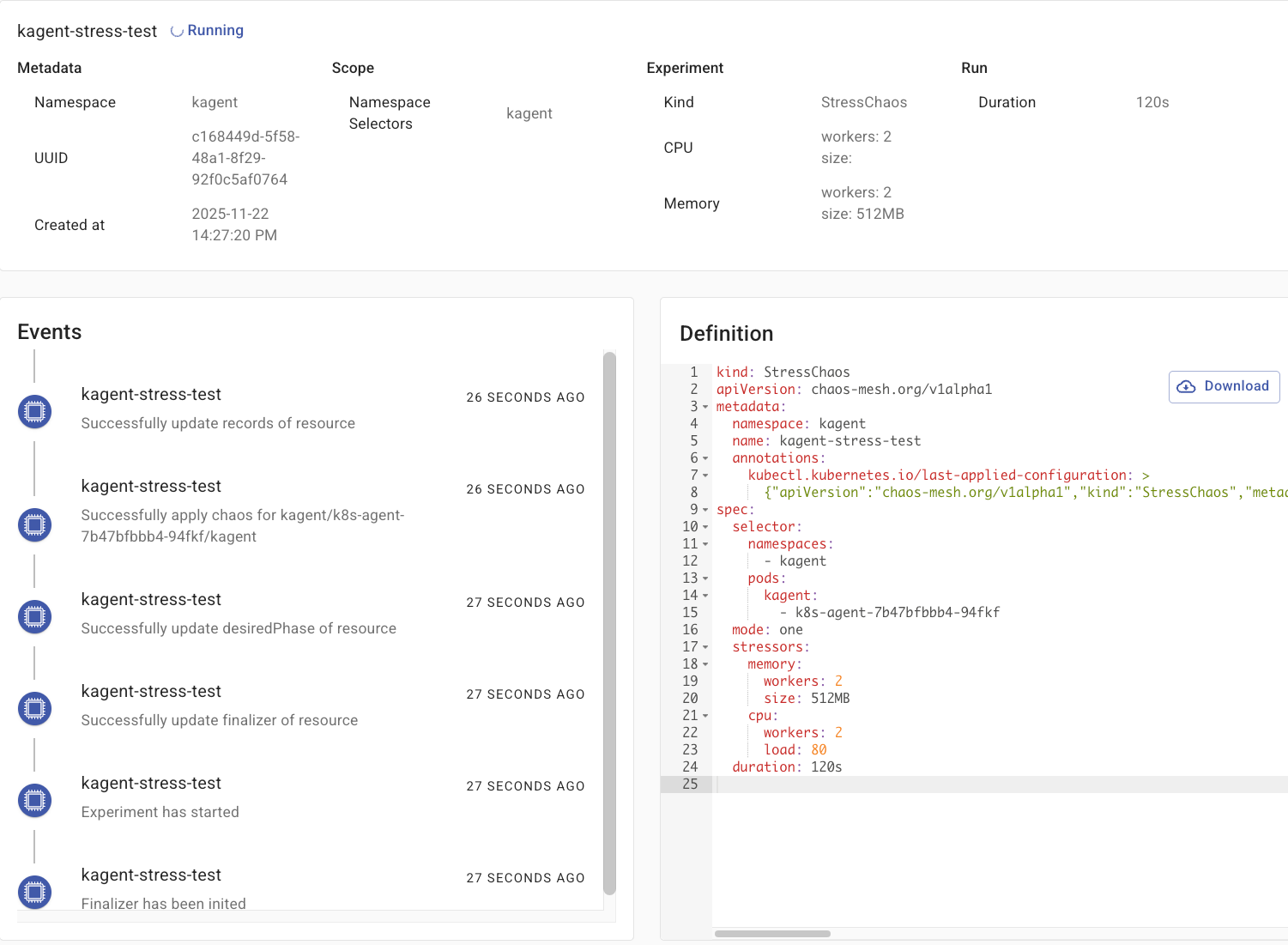
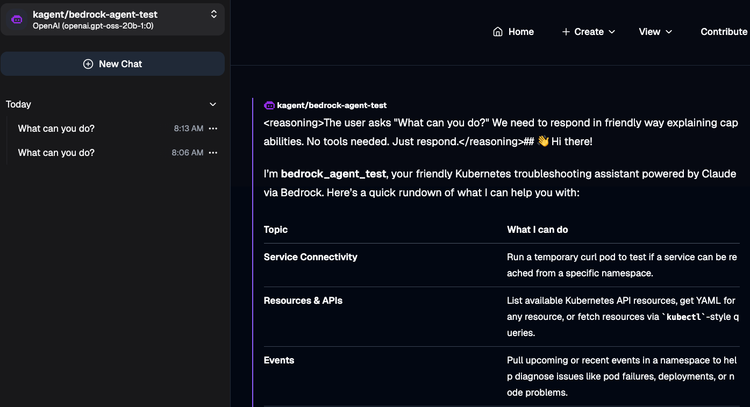
- While the stress test is running, open up the kagent dashboard, go to your k8s-agent Agent, and test it to confirm it is still performing as expected under load.
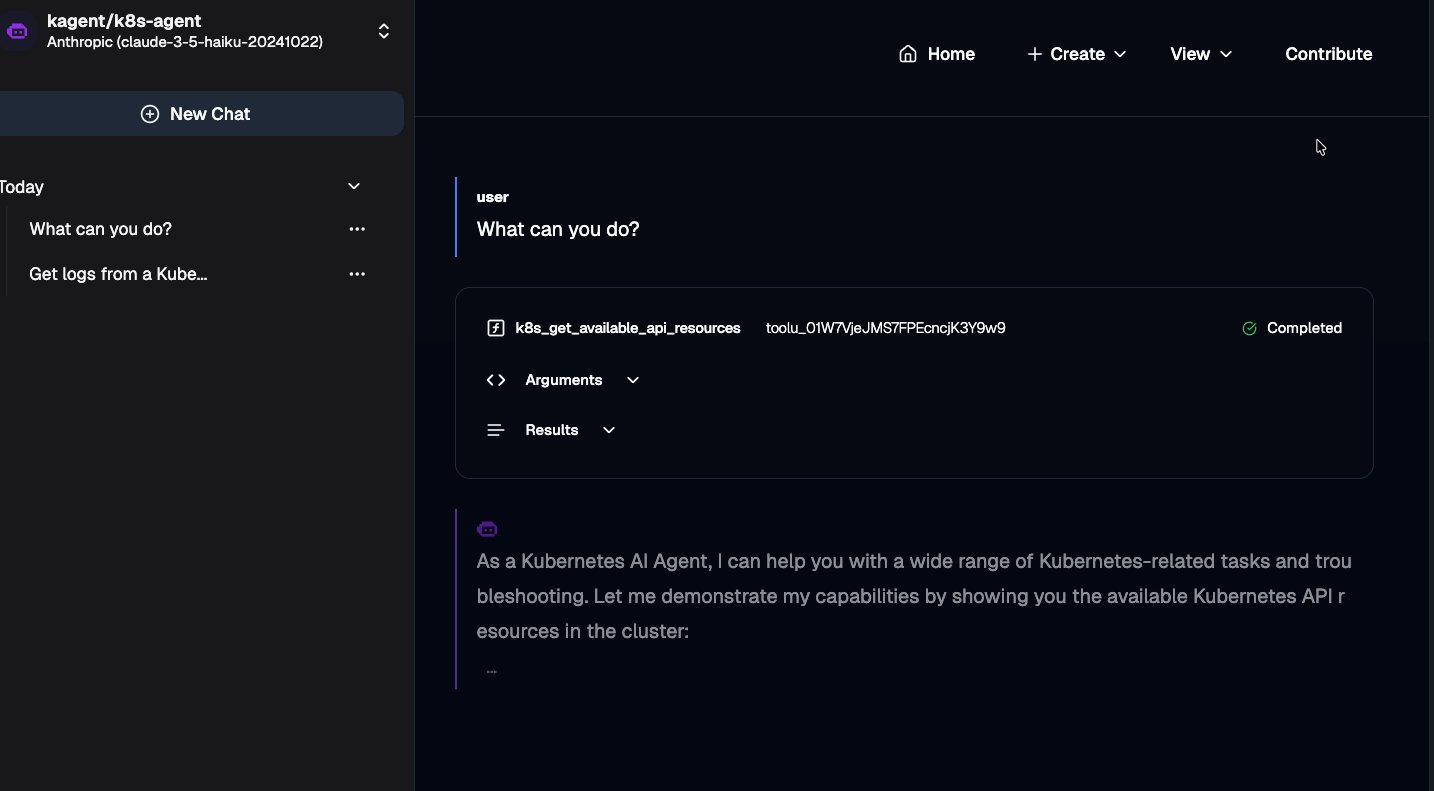
As you can see from the screenshot above and within your kagent environment, the k8s-agent still works as expected.
Testing A Full Failure
The next test to try is to completely destroy the k8s-agent with Chaos Mesh and see if it'll recover. The Agent should recover very quickly because the Agent is running within a Kubernetes Pod, which means the reconciliation loop exists via the ReplicaSet Controller.
- Run the following Experiment.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: chaos-mesh.org/v1alpha1
kind: PodChaos
metadata:
name: kagent-pod-kill
namespace: kagent
spec:
action: pod-kill
mode: one
selector:
namespaces:
- kagent
pods:
kagent:
- k8s-agent-7b47bfbbb4-94fkf # Replace with your specific pod name
EOF- Run the command below to see the Pods in the kagent Namespace.
kubectl get pods -n kagentYou should see an Agent Pod getting deleted, but a new one automatically coming back up due to the reconciliation loop within the ReplicaSet Controller.
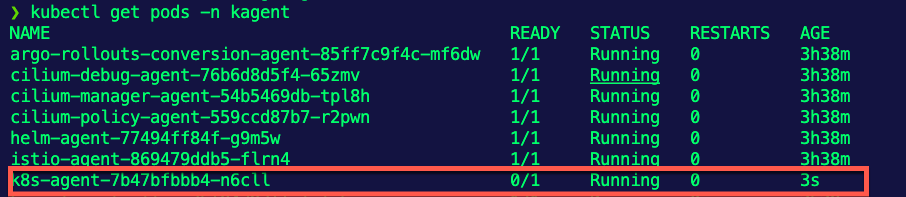
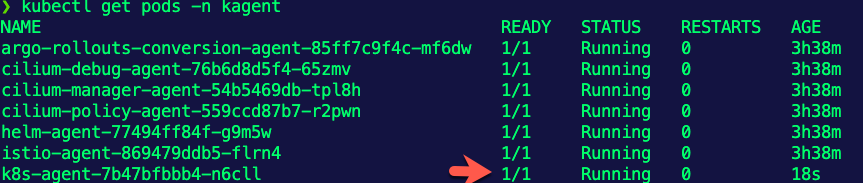
You can also see within the Chaos Mesh dashboard that the experiment ran and completed successfully.
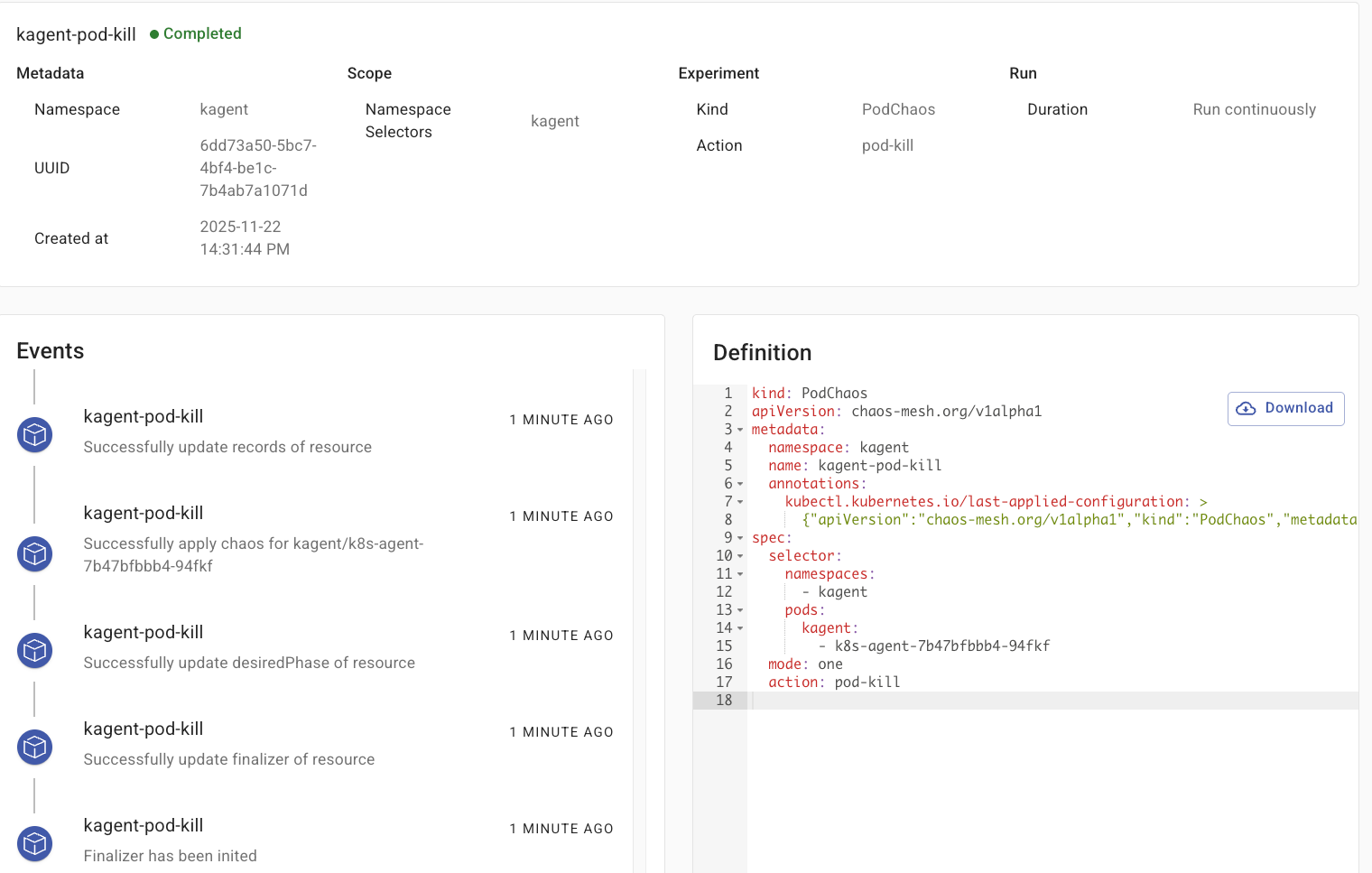

Comments ()