Build AI Agents on Kubernetes: Kagent + Amazon Bedrock Setup Guide
Managing various LLM provider accounts, subscriptions, and cost can get cumbersome for many organizations in a world where multiple LLMs are used. To avoid this, you can use what can be called a "middle ground" between your Agent and the LLM provider.
With AWS Bedrock, you can set up an API key and access various LLMs from Claude to GPT to Llama from one place. Instead of having multiple API keys and various accounts, you can route all of your Agentic traffic from your Agent to an LLM via Bedrock.
In this blog post, you'll learn how to set up an Agent via kagent to access Bedrock Models and use them to perform any action you'd like.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this blog post from a hands-on perspective, you should have the following:
- A Kubernetes cluster.
- Kagent installed, which you can find here.
Configuring Access To AWS
The first step is ensuring that you have proper access to AWS so you can use the Model that you'd like to implement within your Agent.
- Create environment variables with your AWS access key, secret, and region. To retrieve an AWS access key and secret, you'll need to create them in AWS IAM.
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<your-access-key-id>
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<your-secret-access-key>
export AWS_REGION=us-east-1- Once you have access, you can run the command below which will show you what Models are available in your region of choice.
aws bedrock list-inference-profiles --region us-east-1 \
--query "inferenceProfileSummaries[?contains(inferenceProfileId, 'claude')].{id:inferenceProfileId,name:inferenceProfileName}" \
--output tableHere's an example of the output you should see on your terminal.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
| ListInferenceProfiles |
+---------------------------------------------------+----------------------
| id | name |
+---------------------------------------------------+-----------------------
| us.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-20250514-v1:0 | US Claude Sonnet 4 |
| global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0 | Global Claude Sonnet 4.5 |
| us.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0 | US Anthropic Claude Haiku 4.5 |
| global.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0 | Global Anthropic Claude Haiku 4.5 |
| us.anthropic.claude-opus-4-5-20251101-v1:0 | US Anthropic Claude Opus 4.5 |
| global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-5-20251101-v1:0 | GLOBAL Anthropic Claude Opus 4.5 |
| us.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0 | US Anthropic Claude Sonnet 4.5 |
+---------------------------------------------------+------------------------ Next, go into AWS Bedrock and generate an API key. Although you have access to your AWS account, there's a separate API key needed to access LLMs via AWS Bedrock.
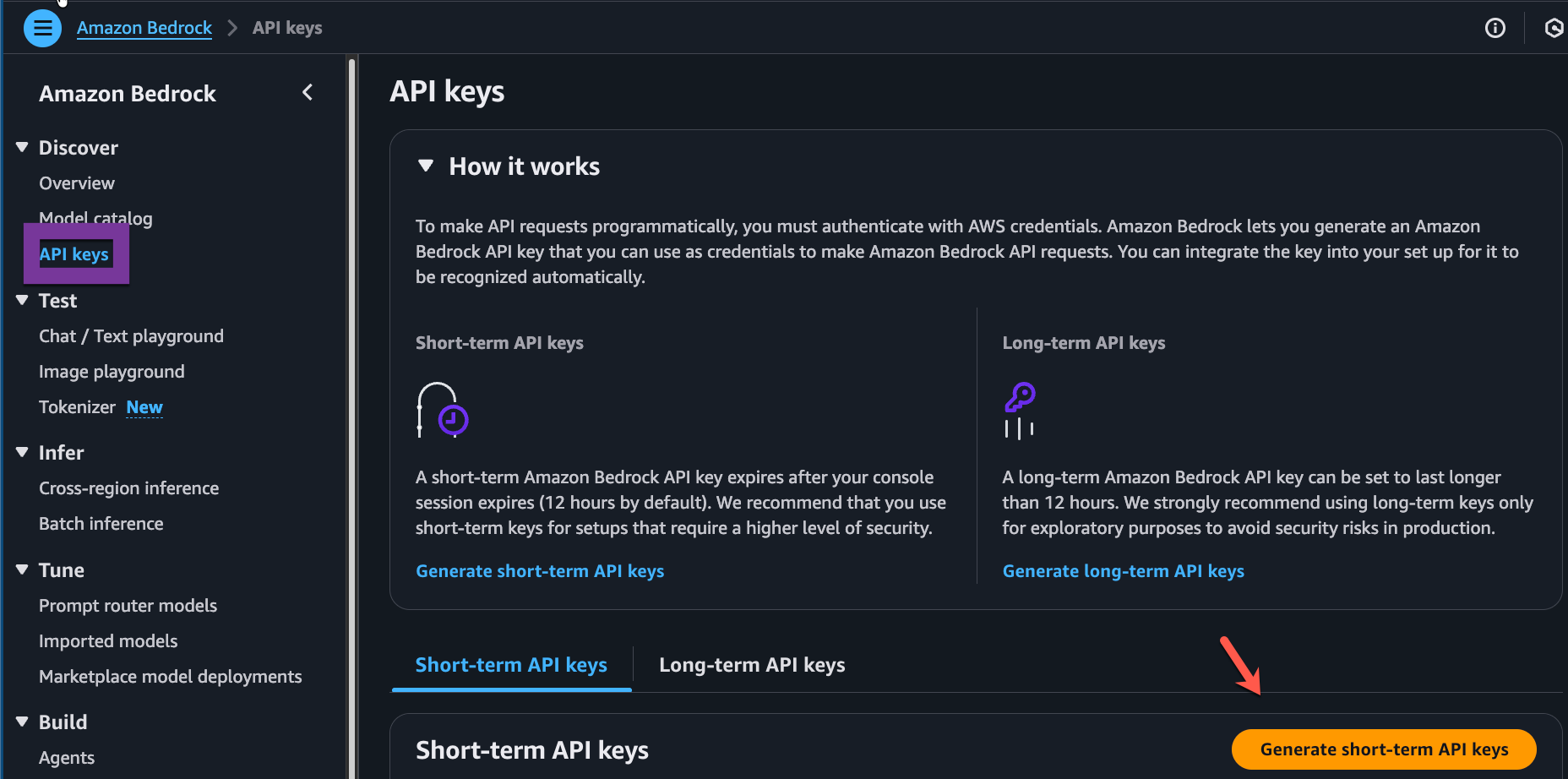
- Create an environment variable with the API key.
export BEDROCK_API_KEY=With this configuration, you can now begin the Model and Agent setup so you can access LLMs via Bedrock through kagent.
Model And Agent Setup
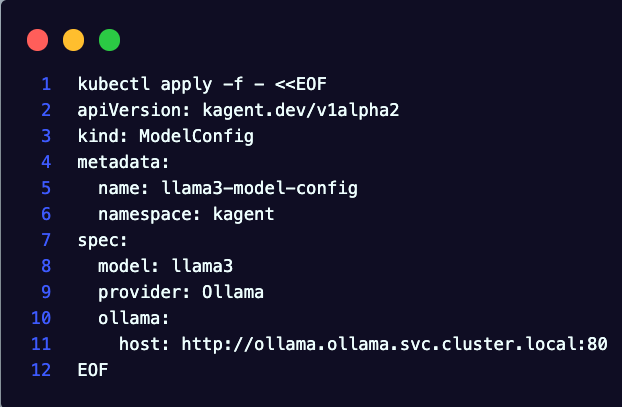
The next phase is to create a Model Config which will be how the Agent knows what Model to access. In this case, the Model called to within the Model Config will be an OpenAI GPT Model.
- Create a Kubernetes secret that contains your AWS access key, secret, and Bedrock API key.
kubectl create secret generic kagent-bedrock-aws -n kagent \
--from-literal=AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID \
--from-literal=AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY \
--from-literal=BEDROCK_API_KEY=$BEDROCK_API_KEY \
--from-literal=AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=""- Implement a Model config that calls out to the
openai.gpt-oss-20b-1:0Model using your Bedrock API key secret. You'll also see the base URL which is the URL where the Model and provider exist via Bedrock.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: kagent.dev/v1alpha2
kind: ModelConfig
metadata:
name: bedrock-model-config
namespace: kagent
spec:
apiKeySecret: kagent-bedrock-aws
apiKeySecretKey: BEDROCK_API_KEY
model: openai.gpt-oss-20b-1:0
provider: OpenAI
openAI:
baseUrl: "https://bedrock-runtime.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/openai/v1"
EOF- Check that the Model was accepted.
kubectl get modelconfig bedrock-model-config -n kagent -o jsonpath='{.status.conditions}' | jqYou'll see an output similar to the below:
[
{
"lastTransitionTime": "...",
"message": "",
"reason": "ModelConfigReconciled",
"status": "True",
"type": "Accepted"
}
]With the Model config set up, you can now create the Agent and test it.
Using Bedrock With Kagent
With kagent installed, you have access to various CRDs like the ModelConfig object you created in the previous section. Within the kagent CRDs, you also have access to the Agent object, which allows you to define everything from what Model Config to use to the prompt to MCP Server tools and Agent Skills.
- Create a new Agent with the YAML below. It includes all of the secrets needed, a prompt, and a few MCP Server tools.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: kagent.dev/v1alpha2
kind: Agent
metadata:
name: bedrock-agent-test
namespace: kagent
spec:
description: Kubernetes troubleshooting agent powered by Claude via Bedrock
type: Declarative
declarative:
modelConfig: bedrock-model-config
deployment:
env:
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: kagent-bedrock-aws
key: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: kagent-bedrock-aws
key: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
- name: AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: kagent-bedrock-aws
key: AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
systemMessage: |
You're a friendly and helpful agent that uses Kubernetes tools to help with troubleshooting and deployments.
# Instructions
- If user question is unclear, ask for clarification before running any tools
- Always be helpful and friendly
- If you don't know how to answer the question, respond with "Sorry, I don't know how to answer that"
# Response format
- ALWAYS format your response as Markdown
- Include a summary of actions you took and an explanation of the result
tools:
- type: McpServer
mcpServer:
name: kagent-tool-server
kind: RemoteMCPServer
toolNames:
- k8s_get_available_api_resources
- k8s_get_cluster_configuration
- k8s_get_events
- k8s_get_pod_logs
- k8s_get_resource_yaml
- k8s_get_resources
- k8s_check_service_connectivity
EOF- Wait until the Agent is up and operational.
kubectl get pods -n kagent --watch- Open the kagent dashboard
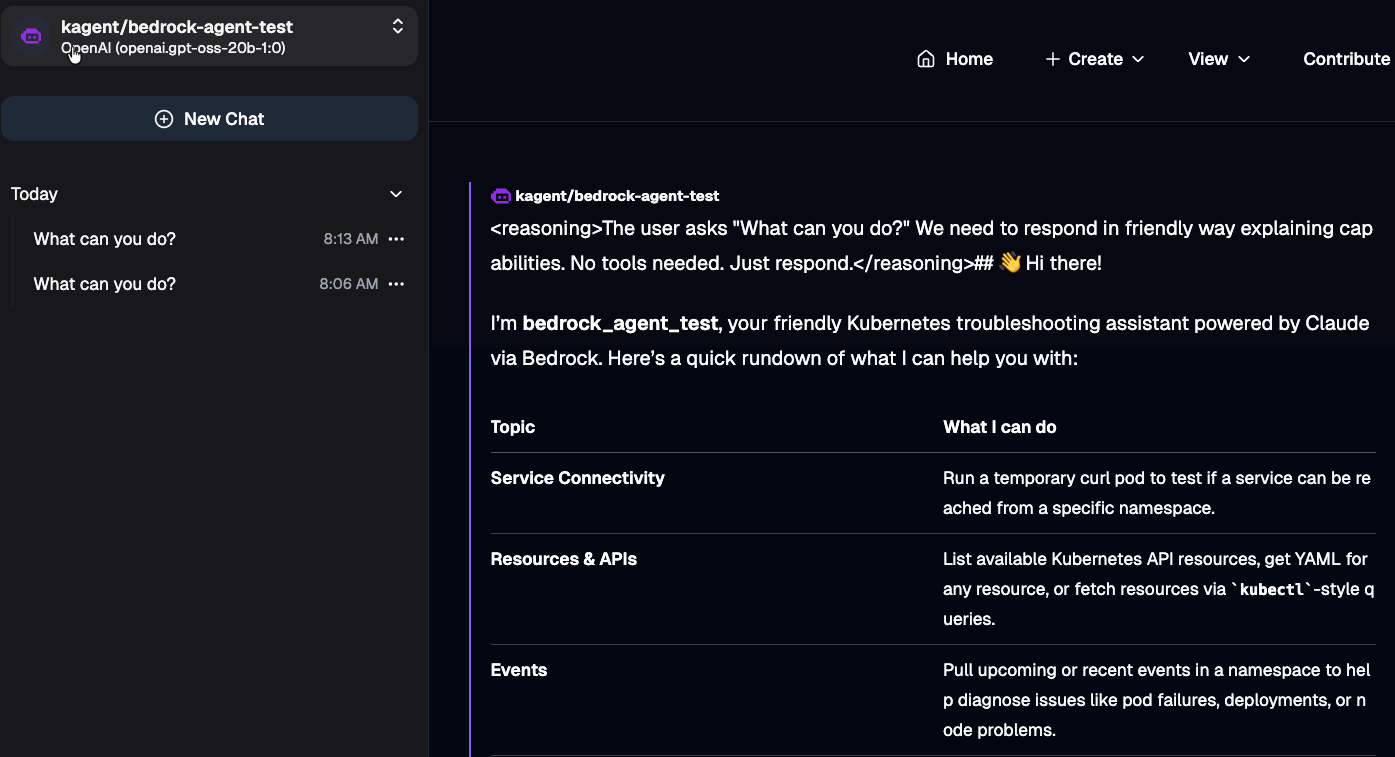
- Go to your new Agent.
- Prompt it with something like
What can you do?. You'll see an output similar to the one below.

Comments ()