Context-Aware Networking & Runtimes: Agentic End-To-End
AI network traffic can very much feel like a black box. You open an AI provider console or an Agent, ask a question or perform a task, and then what happens? Where does that traffic go? Is the traffic secure? Is it going to the appropriate destination? Where’s the context?
There are, what feels like hundreds of questions that need to be answered from when an Agent makes a call to an LLM to when you get a response.
For those questions to be answered, you need an end-to-end workflow for when traffic leaves the Agent to when you get a response or a task is completed.
In this blog post, you’ll learn how to, from a hands-on perspective, accomplish answering those questions.
Install Kagent
The first step in the process is the installation of the two platforms you'll be using, which is kagent and agentgateway. Agentgateway will be installed in the next section and in this section, you'll deploy kagent, which is an Agent framework that runs on Kubernetes.
- Install the kagent CRDs and create the
kagentNamespace.
helm install kagent-crds oci://ghcr.io/kagent-dev/kagent/helm/kagent-crds \
--namespace kagent \
--create-namespace- Specify your AI provider API key. For the purposes of this blog post, Anthropic is used. However, you can use whichever provider you'd like that's supported.
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your_api_key- Install kagent with your specified provider.
helm upgrade --install kagent oci://ghcr.io/kagent-dev/kagent/helm/kagent \
--namespace kagent \
--set providers.default=anthropic \
--set providers.anthropic.apiKey=$ANTHROPIC_API_KEY \
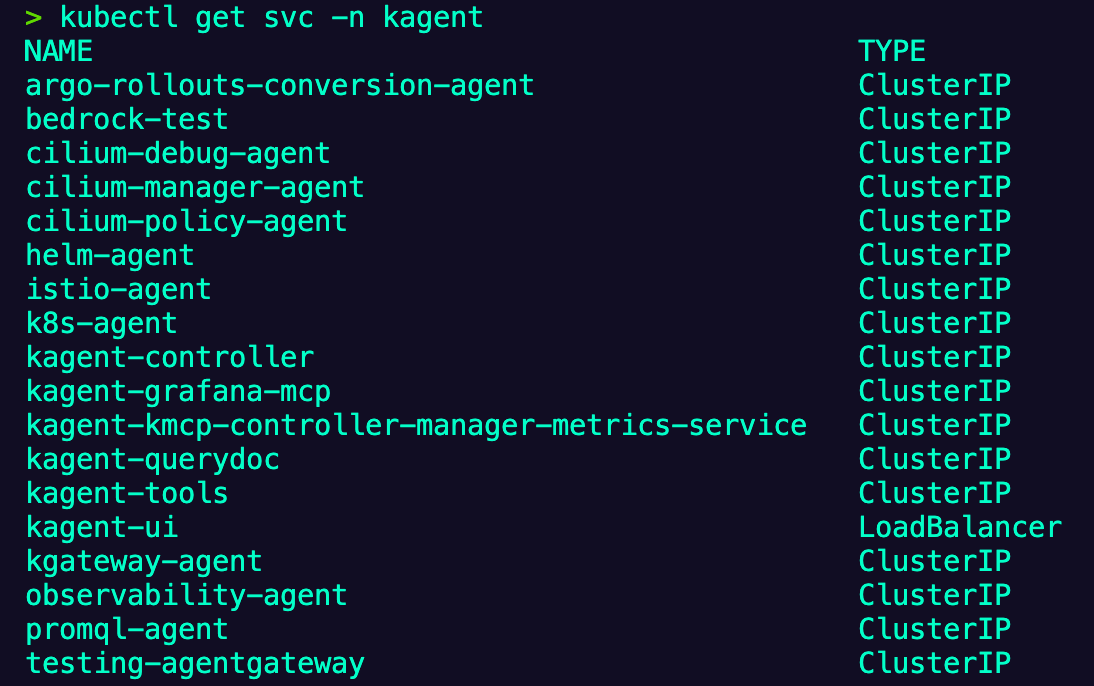
--set ui.service.type=LoadBalancer- Ensure that kagent is installed successfully.
kubectl get svc -n kagentYou should see an output similar to the below.
Install Agentgateway + Kgateway
The next step in the process is to install kgateway with agentgateway enabled. Kgateway is the control plane (think of it as the brains of the operation) and agentgateway is the AI-enabled data plane/proxy for all agentic traffic. You'll see how you can track, observe, and secure all traffic going through an AI Agent with agentgateway.
- Installed the Kubernetes Gateway API CRDs as the Gateway is build with these CRDs to ensure flexibility and agnostic compatibilty.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/releases/download/v1.4.0/standard-install.yaml
- Install the kgateway CRDs.
helm upgrade -i --create-namespace --namespace kgateway-system kgateway-crds oci://cr.kgateway.dev/kgateway-dev/charts/kgateway-crds \
--version v2.1.1 \
--set controller.image.pullPolicy=Always- Install kgateway as the control plane along with agentgateway enabled for AI-related data plane/proxy traffic.
helm upgrade -i -n kgateway-system kgateway oci://cr.kgateway.dev/kgateway-dev/charts/kgateway \
--version v2.1.1 \
--set agentgateway.enabled=true \
--set controller.image.pullPolicy=Always- Ensure that kgateways control plane was installed successfully by checking to see if the kgateway Pod is running.
kubectl get pods -n kgateway-system- The gateway classes for both kgateway (standard Envoy/stateless traffic) and agentgateway (AI-related/stateful traffic) should now be available.
kubectl get gatewayclassYou should see an output similar to the below.
NAME CONTROLLER ACCEPTED AGE
agentgateway kgateway.dev/agentgateway True 20h
kgateway kgateway.dev/kgateway True 20hLLM Gateway Creation
Now that the installation of both the AI Agent framework (kagent) and the AI gateway (agentgateway) is installed, it's time to start the configuration for LLM-related traffic. Any time that you use an AI Agent in kagent, you can observe and secure that traffic via agentgateway. Think of agentgateway as the path that gets your AI traffic from point A to point B.
- Create the secret for your AI provider. In this case, Anthropic is used.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: anthropic-secret
namespace: kagent
labels:
app: agentgateway
type: Opaque
stringData:
Authorization: $ANTHROPIC_API_KEY
EOF- Create a Gateway using agentgateway as the data plane/proxy. When the Gateway is fully up and running, it should have a public IP address if you're on a managed Kubernetes cluster. If you aren't, you'll want to
port-forwardthe Gateway service to be used in the next section. You can find out by runningkubectl get svc -n kgateway-system.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
kind: Gateway
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: agentgateway
namespace: kgateway-system
labels:
app: agentgateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: agentgateway
listeners:
- protocol: HTTP
port: 8080
name: http
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
EOF- The Backend is used to tell the gateway what/where to route to. In this case, you'll be routing to an LLM.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1
kind: Backend
metadata:
labels:
app: agentgateway
name: anthropic
namespace: kgateway-system
spec:
type: AI
ai:
llm:
anthropic:
authToken:
kind: SecretRef
secretRef:
name: anthropic-secret
model: "claude-3-5-haiku-latest"
EOF- Ensure that the backend was deployed successfully.
kubectl get backend -n kgateway-system- The last step is to create a route. The gateway and the backend are both configured, but when you hit the Gateway, there's no configuration to tell the Gateway where to route to. This is where the
HTTPRouteobject comes into play.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: claude
namespace: kgateway-system
labels:
app: agentgateway
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: agentgateway
namespace: kgateway-system
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /anthropic
filters:
- type: URLRewrite
urlRewrite:
path:
type: ReplaceFullPath
replaceFullPath: /v1/chat/completions
backendRefs:
- name: anthropic
namespace: kgateway-system
group: gateway.kgateway.dev
kind: Backend
EOFIn the next section, you'll see how to create and connect an Agent.
Creating and Connecting An Agent
With the Gateway created and traffic flow enabled to flow through the agentgateway proxy, you can create an Agent which will route all packets through agentgateway.
- Create the Model Config which adds the usage of Claude (or any other LLM) to an Agent that can consume it in kagent. Notice how the
baseUrlpoints to the agentgateway IP. The agentgateway IP was created when you ran theGatewayobject in the previous section. As mentioned in the previous section, if you aren't using a managed k8s cluster, you'll want toport-forwardthe Gateway service so it can be accessed as the proxy.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: kagent.dev/v1alpha2
kind: ModelConfig
metadata:
name: anthropic-model-config
namespace: kagent
spec:
apiKeySecret: anthropic-secret
apiKeySecretKey: Authorization
model: claude-3-5-haiku-latest
provider: OpenAI
openAI:
baseUrl: http:YOUR_AGENTGATEWAY_IP:8080/anthropic
EOF/v1/chat/completions is an OpenAI schema. We're using the schema, but the backend is still connecting to a Claude model.- Create the Agent which connects to the Model Config.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: kagent.dev/v1alpha2
kind: Agent
metadata:
name: testing-agentgateway
namespace: kagent
spec:
description: This agent can use a single tool to expand it's Kubernetes knowledge for troubleshooting and deployment
type: Declarative
declarative:
modelConfig: anthropic-model-config
systemMessage: |-
You're a friendly and helpful agent that uses the Kubernetes tool to help troubleshooting and deploy environments
# Instructions
- If user question is unclear, ask for clarification before running any tools
- Always be helpful and friendly
- If you don't know how to answer the question DO NOT make things up
respond with "Sorry, I don't know how to answer that" and ask the user to further clarify the question
# Response format
- ALWAYS format your response as Markdown
- Your response will include a summary of actions you took and an explanation of the result
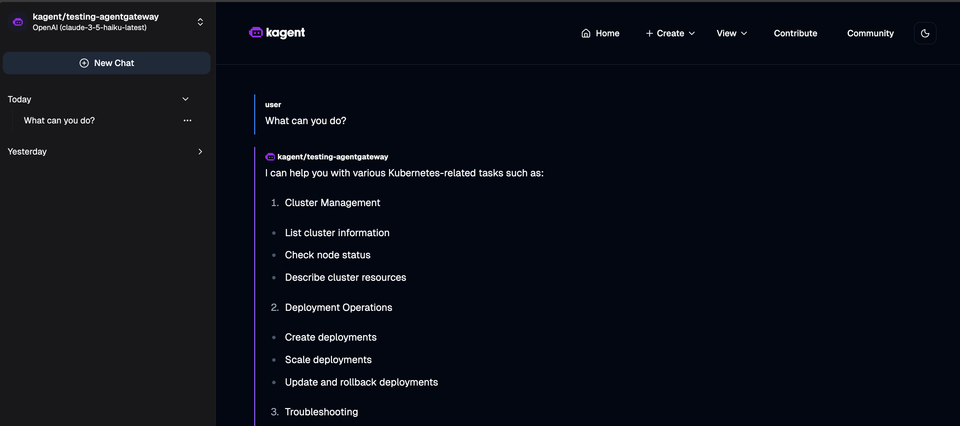
EOF- Open kagent and find the
testing-agentgatewayAgent.
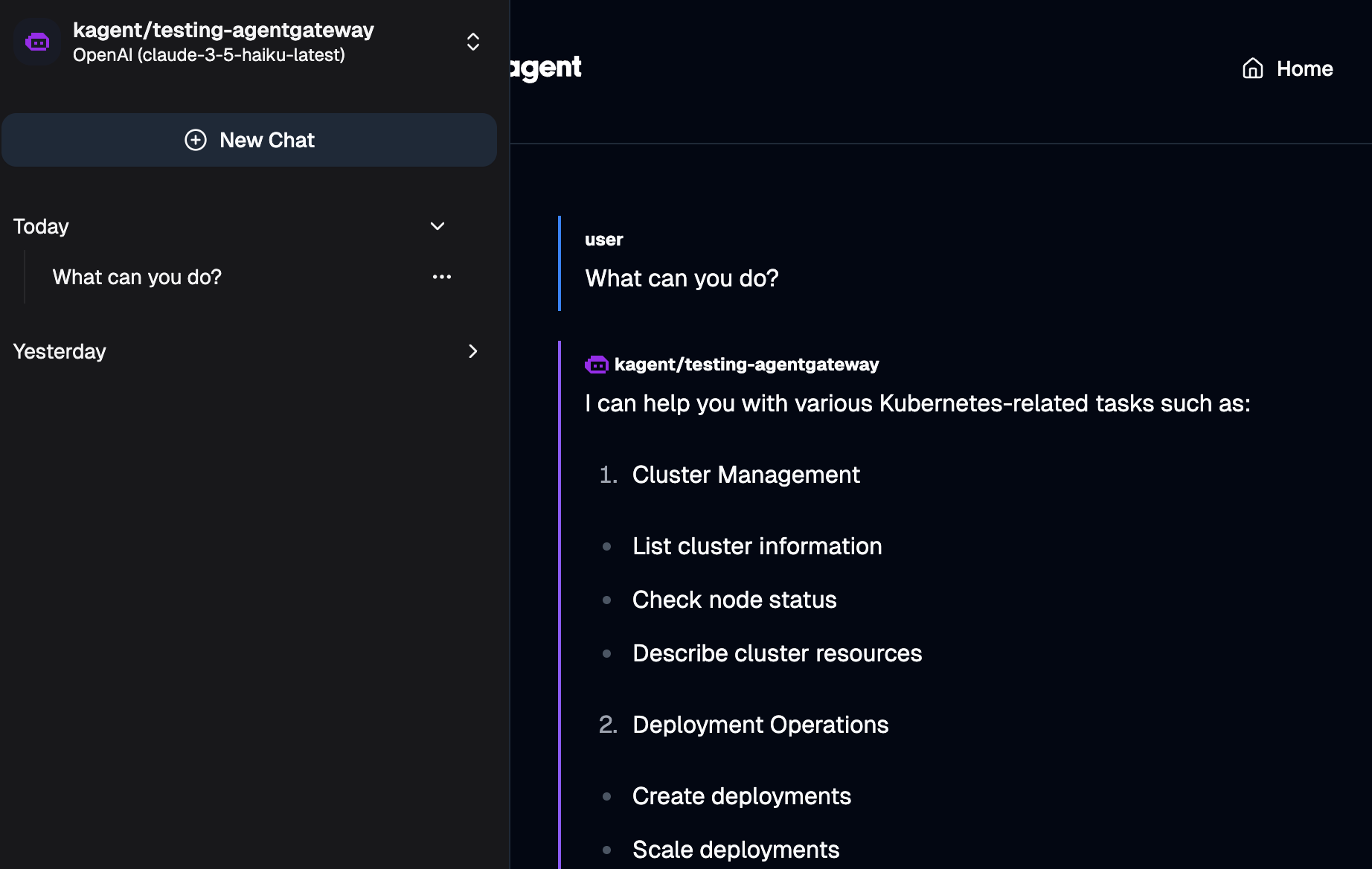
- Prompt the Agent with
What can you do?. You should see an output similiar to the below.
- Open a terminal and run the following commands:
kubectl get pods -n kgateway-system
kubectl logs YOUR_AGENTGATEWAY_POD_NAME -n kgateway-systemYou'll now be able to see that the traffic routed through the agentgateway proxy.
request gateway=kgateway-system/agentgateway listener=http route=kgateway-system/claude endpoint=api.anthropic.com:443 src.addr=192.168.46.17:29426 http.method=POST http.host=a1e5a3b9a8eba4aa09517966f1777763-34157947.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com http.path=/anthropic/chat/completions http.version=HTTP/1.1 http.status=200 protocol=llm gen_ai.operation.name=chat gen_ai.provider.name=anthropic gen_ai.request.model=claude-3-5-haiku-latest gen_ai.response.model=claude-3-5-haiku-20241022 gen_ai.usage.input_tokens=183 gen_ai.usage.output_tokens=240 duration=4797ms

Comments ()